In addition to dry air, the air also contains water vapor. We usually call the mixture of dry air and water vapor wet air (air for short). The content of water vapor in the wet air is minimal. It comes from the evaporation of water on the surface of oceans, rivers, and lakes, and the physiological and technological production processes of various organisms (people, animals, plants, etc.).
Air in nature is a mixture of dry air with a basically stable quantity and water vapor with a constantly changing amount. This mixture is called wet air, also known as air.

Introduction to wet air
1. Dry air
Dry air is the main component of wet air. It is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some rare gases (such as argon, neon, etc.) in a certain proportion.
2. Water vapor
The content of water vapor in the air is constantly changing, usually accounting for several thousandths to twenty-thousandths of the air quality ratio. The air in nature contains some water vapor more or less, so the air in nature is wet air. Absolute dry air does not exist in nature. The air regulated in the air conditioner is wet air.
3. Saturated air
Dry air has the ability to absorb and contain water vapor, and a certain amount of water vapor. We call the air when the content of water vapor reaches the maximum at a certain temperature as saturated air. The corresponding temperature is the saturation temperature of the air. If the saturation temperature of the air is reduced, the water vapor content in the air will also decrease, and the excess water vapor will condense into a liquid. The dewing phenomenon in nature is this reason.
State parameters of wet air
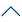
Dry bulb temperature: a scale indicating the degree of air cooling and heating.
Wet bulb temperature: the temperature measured by a wet bulb thermometer. Due to the humidity difference between the wet gauze and the air, the moisture diffuses into the air, vaporizes, and absorbs heat, so the temperature of the wet gauze and thermometer decreases. The temperature at the time of moisture diffusion equilibrium is the wet bulb temperature.
Dew point: There is a limit to the amount of water vapor that can be contained in the air. The higher the temperature, the greater the maximum allowable water vapor content, usually unsaturated wet air. Unsaturated wet air in any state will gradually reduce its temperature under the condition of constant water content. When the temperature is lower than a certain critical temperature, the water vapor in the air will start to condense into water droplets, which is called the dew point temperature of the state point.
Relative humidity: the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor in the air to the partial pressure of saturated water vapor at the same temperature is the relative humidity.
Relative humidity indicates the degree to which the air is close to saturation. The smaller the value is, the drier the air is and the stronger the ability of the air to absorb water vapor. The higher the value, the more humid the air is, the closer it is to saturation, and the weaker the air’s ability to absorb water vapor. 0 is dry air and 100% is saturated wet air.
Moisture content: the mass of water vapor contained in 1kg dry air is called moisture content, unit: g/kg.
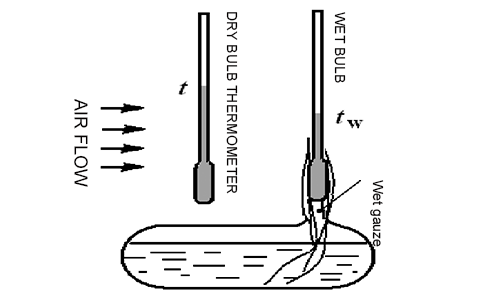
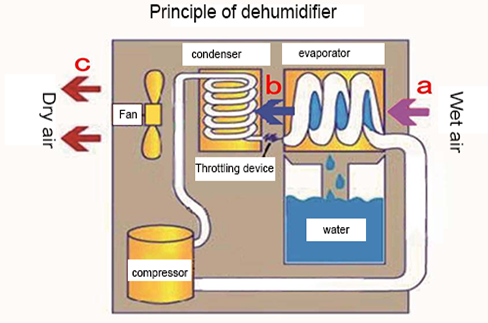
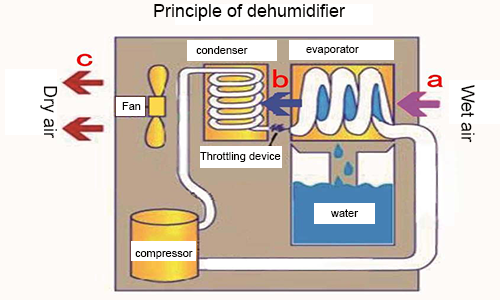
Working principle of the dehumidifier
The wet air passes through the evaporator, cools down from a point along the iso-humidity line to 100% saturated humidity line (dew point temperature), then begins to precipitate water droplets, continues to cool down, and dehumidify along the saturated humidity line to point b, and then enters the condenser, and rises up from point b along the iso-humidity line to point c, and then exits the dehumidifier.
Post time: Feb-13-2023
 +86-13376814803
+86-13376814803  robert@hzhongtai.com
robert@hzhongtai.com